Aphids life cycle pdf Bay of Plenty

Aphids firstrays.com Life cycle of aphids. A generation of aphids survives the winter as eggs, which allows them to withstand extreme environmental conditions of temperature and moisture. In spring the eggs on the plant (primary host) hatch, leading to the first generation of aphids. All …
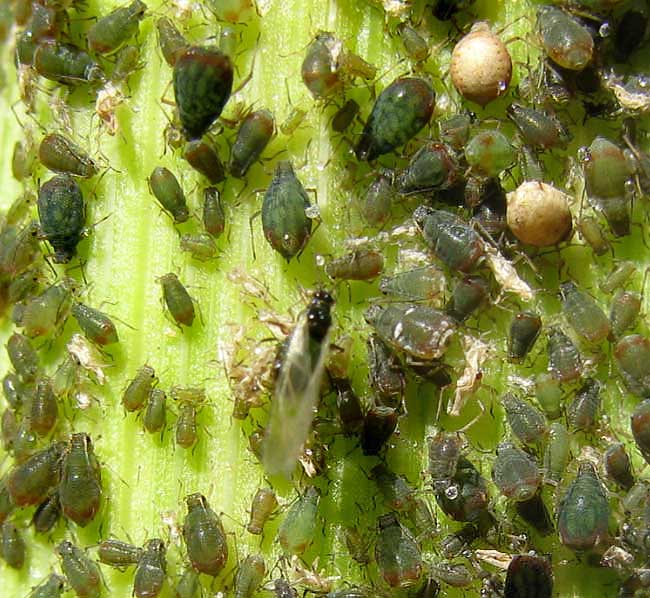
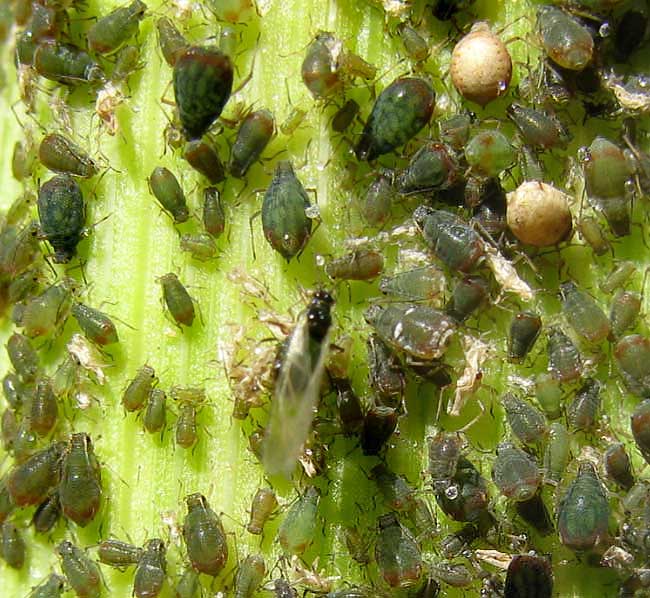
Rhopalosiphum padi (Bird cherry oat aphid
The Aphid Life Cycle Backyard Nature. 24.06.2008В В· Some species can produce up to eight different alternative morphs, all genetically identical, during their life-cycle. Polyphenisms result from alternative modes of development induced in response to specific environmental cues. For example, most aphids develop without wings, investing the extra resources in more offspring., 21.03.2016В В· The life cycle, genetic diversity, and genetic structure of R. padi populations throughout China remain unclear. In the current study, we collected 17 R. padi populations throughout the wheat-growing region of China. Classical standard methods were used to determine the life cycles of 369 clones from the sampled populations..
Some Background. Aphids, members of the order Homoptera, are probably the most notorious pests in the world. With well over 4000 species of aphids in this huge order, there is an aphid for everyone and nearly everyone in horticulture and agriculture may have to, at some point in time, deal with aphids. Aphids have complex and varied life cycles. Aphid colonies on cruciferous crops consist mainly of wingless females and nymphs during most of the growing season. entire life cycle can be completed within a few weeks, or it may require up to 2 months, depending on the temperature. Figure 1.
•The life cycle of honey bees begins when an egg hatches. •During the first stage of its development, the offspring form a digestive system, a nervous system and an outer covering (the exoskeleton). •Each member of a colony develops, after hatching, as an adult over varying durations: –Queens become full-grown adults within 16 days, Life cycle of the cereal aphid Sitobion avenae F.: Polymorphism and comparison of life history traits associated with sexuality. It overwinters on Poaceae species where the sexual cycle occurs, even though aphids can continue reproducing parthenogenetically all the year.
Some Background. Aphids, members of the order Homoptera, are probably the most notorious pests in the world. With well over 4000 species of aphids in this huge order, there is an aphid for everyone and nearly everyone in horticulture and agriculture may have to, at some point in time, deal with aphids. In the process of sucking out plant juices, aphids- like mealybugs and scale - excrete a sweetish, sticky "honeydew" that often turns a moldy black and may lure ants. Aphids also carry viral diseases to plants. Life cycle: Females seem to like enormous families. A single aphid typically gives birth to
The life-cycle and behaviour of aphids. Reproduction, feeding, damage to plants, and control of damage. Accompanied by detailed biological drawings. Biology teaching resources by D G Mackean Life cycle . All aphids are females and can live for 28 days. When they reproduce they reproduce viviparous and lay female aphids alive an\൤ ready to feed. They then go through 4 nymphal stages and become adults in 5 days in which then those females can start reprodu對cing more female aphids.
11.11.2019В В· A defining characteristic of the anholocyclic life cycle Who's involved in the holocyclic life cycle Skills Practiced. Information recall - access the knowledge you have gained about the concept of host changing in aphids Reading comprehension - ensure that you draw the most important details from the lesson on aphids and their reproduction Although aphids cannot fly for most of their life cycle, they can escape predators and accidental ingestion by herbivores by dropping off the plant onto the ground. Others species use the soil as a permanent protection, feeding on the vascular systems of roots and remaining underground all their lives.
In the process of sucking out plant juices, aphids- like mealybugs and scale - excrete a sweetish, sticky "honeydew" that often turns a moldy black and may lure ants. Aphids also carry viral diseases to plants. Life cycle: Females seem to like enormous families. A single aphid typically gives birth to Some Background. Aphids, members of the order Homoptera, are probably the most notorious pests in the world. With well over 4000 species of aphids in this huge order, there is an aphid for everyone and nearly everyone in horticulture and agriculture may have to, at some point in time, deal with aphids.
Aphids have complex and varied life cycles. Aphid colonies on cruciferous crops consist mainly of wingless females and nymphs during most of the growing season. entire life cycle can be completed within a few weeks, or it may require up to 2 months, depending on the temperature. Figure 1. The black bean aphid has both sexual and asexual generations in its life cycle. It also alternates hosts at different times of year. The primary host plants are woody shrubs, and eggs are laid on these by winged females in the autumn. The adults then die and the eggs overwinter.
Though aphids cannot fly for most of their life cycle, they can escape predators and accidental ingestion by herbivores by dropping off the plant they are on. Some species of aphid, known as "woolly aphids" (Eriosomatinae), excrete a "fluffy wax coating" for protection. Annual Review of Entomology Aphid Ecology: Life Cycles, Polymorphism, and Population Regulation A. F. G. Dixon Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics HOST PLANT SELECTION BY APHIDS: Behavioral, Evolutionary, and Applied Perspectives Glen Powell, Colin R. Tosh, and Jim Hardie Annual Review of Entomology Biology of Aphids
The seasonal life cycle of the soybean aphid is complex with up to 18 generations a year. It requires two species of host plant to complete its life cycle: common buckthorn and soybean. Common buckthorn is a woody shrub or small tree and is the overwintering host plant of the aphid. Soybean aphids lay eggs on buckthorn in the fall. Aphid egg production. Whilst the great majority of individual aphids are parthenogenetic, nearly every species of aphid can lay fertilized eggs. The aphid eggs described below are of Aphidoidea, which includes the Aphididae (or 'true aphids'), Adelgidae (sometimes …
21.03.2016 · The life cycle, genetic diversity, and genetic structure of R. padi populations throughout China remain unclear. In the current study, we collected 17 R. padi populations throughout the wheat-growing region of China. Classical standard methods were used to determine the life cycles of 369 clones from the sampled populations. 10.02.2010 · Life cycle changes, whether corresponding to the loss or acquisition of a primary host, necessarily promote speciation, by inducing shifts of the reproductive phase on different plants. We suggest that the evolutionary lability of life cycle may have driven speciation events in …
LIFE CYCLE OF THE HONEY BEE WordPress.com

Aphid insect Britannica. Life cycle of the cereal aphid Sitobion avenae F.: Polymorphism and comparison of life history traits associated with sexuality. It overwinters on Poaceae species where the sexual cycle occurs, even though aphids can continue reproducing parthenogenetically all the year., Aphid egg production. Whilst the great majority of individual aphids are parthenogenetic, nearly every species of aphid can lay fertilized eggs. The aphid eggs described below are of Aphidoidea, which includes the Aphididae (or 'true aphids'), Adelgidae (sometimes ….
LIFE CYCLE OF THE SUGARBEET ROOT APHID

4. the Life Cycle of Aphids and Coccids.* Annals of the. aphids, which can become mature adults within a couple of weeks or so after birth. (Development is always strongly related to temperature.) Adult females may give birth to perhaps 1-5 young per day for their remaining life, which likely will normally be short, perhaps a 3 … aphids, which can become mature adults within a couple of weeks or so after birth. (Development is always strongly related to temperature.) Adult females may give birth to perhaps 1-5 young per day for their remaining life, which likely will normally be short, perhaps a 3 ….
As cannabis aphids grow they must periodically shed their external "skin" (exoskeleton) and as they produce a new and larger exoskeleton for the next, larger life stage. These "cast skins" will collect around colonies of aphids and often drop onto leaves below an aphid … Insect Order ID: Hemiptera (Aphids) Life Cycle –A form of gradual metamorphosis (also called incomplete or simple). Eggs hatch in spring producing parthenogenic females (able to reproduce asexually), which give birth to live young within a few days after birth.
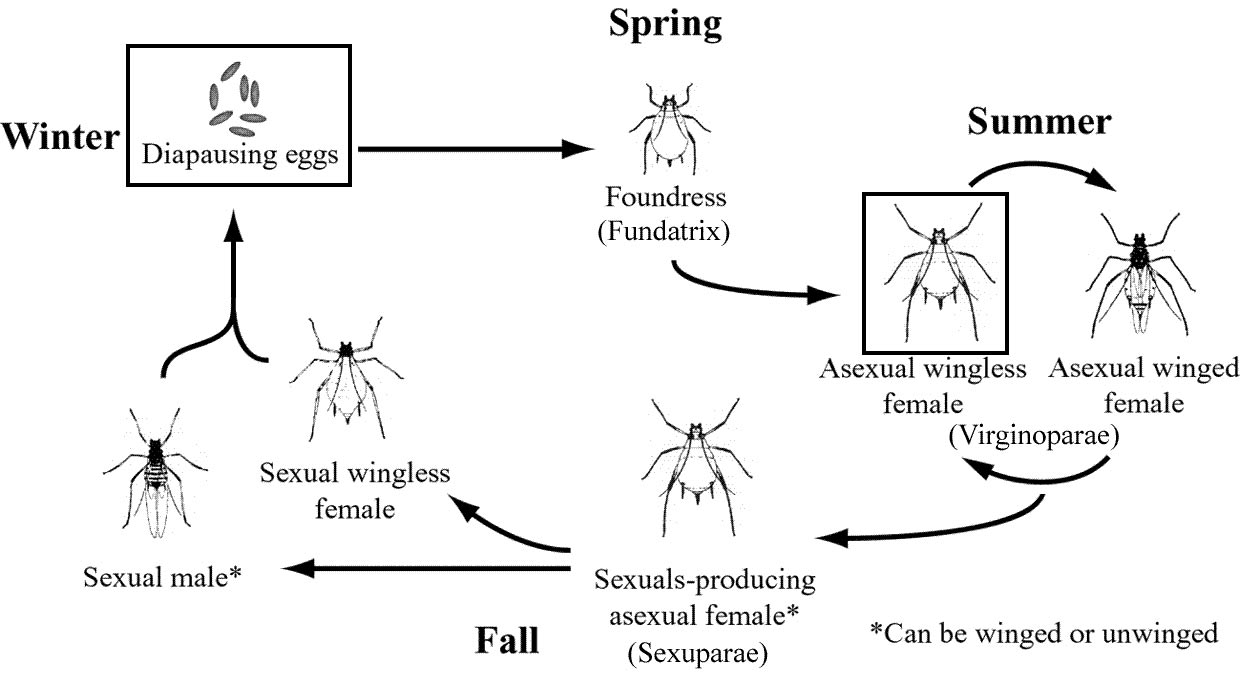
The life cycle of many aphids is somewhat unusual and complex. Most species overwinter in the egg stage on the host plant; the eggs hatch into young female nymphs (stem mothers) in the spring, and subsequently reproduce without mating (parthenogenetic reproduction), giving birth to living young. 12.05.2016 · Aphids inflict serious damage to a variety of crops. They are notorious virus vectors and have an enormous reproductive capacity. There are lots of different coloured species and they occur in all kinds of crops. The …
Aphids have a short life cycle and can produce a large number of generations each year. It takes roughly eight days for an aphid to reach adulthood. Female aphids stay in … aphids, which can become mature adults within a couple of weeks or so after birth. (Development is always strongly related to temperature.) Adult females may give birth to perhaps 1-5 young per day for their remaining life, which likely will normally be short, perhaps a 3 …
3. Reciprocal crosses within and between life cycle variants showed no effect of the type of cross on the number of eggs laid per mating female, their hatching success, or the survival and fecundity of the parthenogenetic females born from eggs (fundatrices). 4. ENTFACT-219: Woolly Apple Aphid Download PDF. by Ric Bessin, Extension Entomologist, and John Hartman, Extension Plant Pathologist University of Kentucky College of Agriculture The woolly apple aphid differs from other apple aphids in appearance, life cycle, and the type of damage inflicted.
3. Reciprocal crosses within and between life cycle variants showed no effect of the type of cross on the number of eggs laid per mating female, their hatching success, or the survival and fecundity of the parthenogenetic females born from eggs (fundatrices). 4. Though aphids cannot fly for most of their life cycle, they can escape predators and accidental ingestion by herbivores by dropping off the plant they are on. Some species of aphid, known as "woolly aphids" (Eriosomatinae), excrete a "fluffy wax coating" for protection.
Aphids have a short life cycle and can produce a large number of generations each year. It takes roughly eight days for an aphid to reach adulthood. Female aphids stay in … Aphids suck on sap, causing loss of vigour, and in some cases yellowing, stunting or distortion of plant parts. Honeydew (unused sap) secreted by the insects can cause sooty mould to develop on leaves. In crops such as cotton, the honeydew affects fibre quality. Aphids can also be vectors (carriers) for viruses.
aphids, which can become mature adults within a couple of weeks or so after birth. (Development is always strongly related to temperature.) Adult females may give birth to perhaps 1-5 young per day for their remaining life, which likely will normally be short, perhaps a 3 … Identification of some common aphids: Aphids are all generally small (1-3mm) and soft bodied, and have a pair of unique structures that resemble "tailpipes" near the end of their abdomen, called cornicles. Adults may or may not have wings. More than 20 aphid species can infest various greenhouse crops.
As cannabis aphids grow they must periodically shed their external "skin" (exoskeleton) and as they produce a new and larger exoskeleton for the next, larger life stage. These "cast skins" will collect around colonies of aphids and often drop onto leaves below an aphid … projections, on the top side of the tail end. Aphids feed singly or in colonies on upper and lower leaf surfaces and stems. They feed near plant bases when plants are young or during cold weather, and on upper-canopy leaves, stems, and even grain heads later in the season. Life Cycle and Injury All four aphid species overwinter in small grains in
Life cycle . All aphids are females and can live for 28 days. When they reproduce they reproduce viviparous and lay female aphids alive an\൤ ready to feed. They then go through 4 nymphal stages and become adults in 5 days in which then those females can start reprodu對cing more female aphids. As cannabis aphids grow they must periodically shed their external "skin" (exoskeleton) and as they produce a new and larger exoskeleton for the next, larger life stage. These "cast skins" will collect around colonies of aphids and often drop onto leaves below an aphid …
12.05.2016 · Aphids inflict serious damage to a variety of crops. They are notorious virus vectors and have an enormous reproductive capacity. There are lots of different coloured species and they occur in all kinds of crops. The … 24.06.2008 · Some species can produce up to eight different alternative morphs, all genetically identical, during their life-cycle. Polyphenisms result from alternative modes of development induced in response to specific environmental cues. For example, most aphids develop without wings, investing the extra resources in more offspring.

Aphids Life Cycle. One of the most potent and dangerous pests on Earth, the key to controlling the population of aphids, lies in the study of their life cycle. Omkar Phatak. Last Updated: Mar 9, 2018. If you make a list of the worst pests worldwide, then aphids will definitely be included in there. To attempt to epitomize the life cycle of the aphid is like trying to draw an orderly sketch of Chaos. But after all, the confusion may be more seeming than real and certain rules, beset though they may be with exceptions, govern the life of even the aphid.
Aphids Life Cycle gardenerdy.com
Cannabis Aphid webdoc.agsci.colostate.edu. into the field, fields will not only be inoculated with aphids but insecticide resistance may be introduced. These aphids also can be transported long distances by wind and storms. Life Cycle and Description The life cycle varies considerably, depending on the pres-ence of cold winters. van Emden et al. (1969) provide a good review of the life, Life cycle . All aphids are females and can live for 28 days. When they reproduce they reproduce viviparous and lay female aphids alive an\൤ ready to feed. They then go through 4 nymphal stages and become adults in 5 days in which then those females can start reprodu對cing more female aphids..
Life cycle of the cereal aphid Sitobion avenae F
Aphid insect Britannica. Life cycle. Bird cherry (Prunus padus) with its long drooping white flowers (below) is the primary host of Rhopalosiphum padi. The eggs of Rhopalosiphum padi are laid in autumn in the narrow gap between the axillary buds and the stem (see image below)., Although aphids cannot fly for most of their life cycle, they can escape predators and accidental ingestion by herbivores by dropping off the plant onto the ground. Others species use the soil as a permanent protection, feeding on the vascular systems of roots and remaining underground all their lives..
LIFE CYCLE OF THE SUGARBEET ROOT APHID . A relatively new pest entered the sugarbeet production cycle and everyone is interested in the economic impact these insects will have on the crop. Sugarbeet aphids feed primarily on the secondary root systems; although heavy 12.05.2016 · Aphids inflict serious damage to a variety of crops. They are notorious virus vectors and have an enormous reproductive capacity. There are lots of different coloured species and they occur in all kinds of crops. The …
Aphids have a complex life cycle. There can be winged and non-winged adults depending on temperature, day length, population level or plant quality. Life cycle duration varies among species and environmental conditions. In greenhouses, aphids reproduce without mating. Aphid egg production. Whilst the great majority of individual aphids are parthenogenetic, nearly every species of aphid can lay fertilized eggs. The aphid eggs described below are of Aphidoidea, which includes the Aphididae (or 'true aphids'), Adelgidae (sometimes …
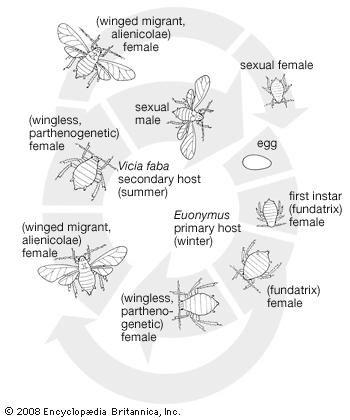
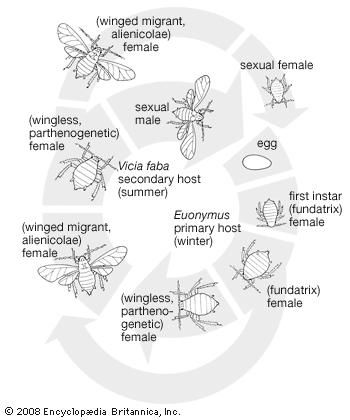
Life cycle of aphids. The life cycle of the aphid is complicated. Wingless females, called stem mothers, reproduce without fertilization (i.e., by parthenogenesis) throughout the summer. These stem mothers are unique in that they produce living young (viviparity) … Life cycle of the cereal aphid Sitobion avenae F.: Polymorphism and comparison of life history traits associated with sexuality. It overwinters on Poaceae species where the sexual cycle occurs, even though aphids can continue reproducing parthenogenetically all the year.
The life-cycle and behaviour of aphids. Reproduction, feeding, damage to plants, and control of damage. Accompanied by detailed biological drawings. Biology teaching resources by D G Mackean Aphids have a complex life cycle. There can be winged and non-winged adults depending on temperature, day length, population level or plant quality. Life cycle duration varies among species and environmental conditions. In greenhouses, aphids reproduce without mating.
The life-cycle and behaviour of aphids. Reproduction, feeding, damage to plants, and control of damage. Accompanied by detailed biological drawings. Biology teaching resources by D G Mackean Aphids are very interesting insects. You will not likely find any aphid eggs because adult aphids grow wings at a certain stage of their life cycle and fly away to lay them. However, you may see small aphids coming out of the rear of a bigger one. This is because adult aphids produce live young aphids that look like adults but are smaller.
Although aphids cannot fly for most of their life cycle, they can escape predators and accidental ingestion by herbivores by dropping off the plant onto the ground. Others species use the soil as a permanent protection, feeding on the vascular systems of roots and remaining underground all their lives. 12.05.2016 · Aphids inflict serious damage to a variety of crops. They are notorious virus vectors and have an enormous reproductive capacity. There are lots of different coloured species and they occur in all kinds of crops. The …
10.02.2010 · Life cycle changes, whether corresponding to the loss or acquisition of a primary host, necessarily promote speciation, by inducing shifts of the reproductive phase on different plants. We suggest that the evolutionary lability of life cycle may have driven speciation events in … The black bean aphid has both sexual and asexual generations in its life cycle. It also alternates hosts at different times of year. The primary host plants are woody shrubs, and eggs are laid on these by winged females in the autumn. The adults then die and the eggs overwinter.
Winged adult green peach aphid, Myzus persicae (Sulzer). Photograph by Lyle J. Buss, University of Florida. Life Cycle and Description (Back to Top) The life cycle varies considerably, depending on the presence of cold winters. van Emden et al. (1969) provide a good review of the life cycle. The seasonal life cycle of the soybean aphid is complex with up to 18 generations a year. It requires two species of host plant to complete its life cycle: common buckthorn and soybean. Common buckthorn is a woody shrub or small tree and is the overwintering host plant of the aphid. Soybean aphids lay eggs on buckthorn in the fall.
ENTFACT-219: Woolly Apple Aphid Download PDF. by Ric Bessin, Extension Entomologist, and John Hartman, Extension Plant Pathologist University of Kentucky College of Agriculture The woolly apple aphid differs from other apple aphids in appearance, life cycle, and the type of damage inflicted. Identification of some common aphids: Aphids are all generally small (1-3mm) and soft bodied, and have a pair of unique structures that resemble "tailpipes" near the end of their abdomen, called cornicles. Adults may or may not have wings. More than 20 aphid species can infest various greenhouse crops.
10.02.2010 · Life cycle changes, whether corresponding to the loss or acquisition of a primary host, necessarily promote speciation, by inducing shifts of the reproductive phase on different plants. We suggest that the evolutionary lability of life cycle may have driven speciation events in … 3. Reciprocal crosses within and between life cycle variants showed no effect of the type of cross on the number of eggs laid per mating female, their hatching success, or the survival and fecundity of the parthenogenetic females born from eggs (fundatrices). 4.
Aphids on Cruciferous Crops oaktrust.library.tamu.edu

Rhopalosiphum padi (Bird cherry oat aphid. In the process of sucking out plant juices, aphids- like mealybugs and scale - excrete a sweetish, sticky "honeydew" that often turns a moldy black and may lure ants. Aphids also carry viral diseases to plants. Life cycle: Females seem to like enormous families. A single aphid typically gives birth to, The black bean aphid has both sexual and asexual generations in its life cycle. It also alternates hosts at different times of year. The primary host plants are woody shrubs, and eggs are laid on these by winged females in the autumn. The adults then die and the eggs overwinter..
LIFE CYCLE OF THE SUGARBEET ROOT APHID. The black bean aphid has both sexual and asexual generations in its life cycle. It also alternates hosts at different times of year. The primary host plants are woody shrubs, and eggs are laid on these by winged females in the autumn. The adults then die and the eggs overwinter., Tulip bulb aphids (Dysaphis tulipae) can infect many different bulbs in storage. Some aphids may even be found on plant roots (Pemphigus species). Honeysuckle aphid Oleander aphid Life Cycle Most types of aphids do not mate and the females give birth to live nymphs. There is no egg stage..
Aphids Business Queensland

Geographic variation and evolution in the life cycle of. Life cycle of the cereal aphid Sitobion avenae F.: Polymorphism and comparison of life history traits associated with sexuality. It overwinters on Poaceae species where the sexual cycle occurs, even though aphids can continue reproducing parthenogenetically all the year. into the field, fields will not only be inoculated with aphids but insecticide resistance may be introduced. These aphids also can be transported long distances by wind and storms. Life Cycle and Description The life cycle varies considerably, depending on the pres-ence of cold winters. van Emden et al. (1969) provide a good review of the life.
Although aphids cannot fly for most of their life cycle, they can escape predators and accidental ingestion by herbivores by dropping off the plant onto the ground. Others species use the soil as a permanent protection, feeding on the vascular systems of roots and remaining underground all their lives. The black bean aphid has both sexual and asexual generations in its life cycle. It also alternates hosts at different times of year. The primary host plants are woody shrubs, and eggs are laid on these by winged females in the autumn. The adults then die and the eggs overwinter.
24.06.2008В В· Some species can produce up to eight different alternative morphs, all genetically identical, during their life-cycle. Polyphenisms result from alternative modes of development induced in response to specific environmental cues. For example, most aphids develop without wings, investing the extra resources in more offspring. The bio-geographical conditions of the host have great influence on the life cycle pattern of aphids. Individual species depicts varied life cycle patterns in different bio-geographical conditions (Moran 1992). Some species lead different patterns of life cycles in the tropics and temperate climate (Blackman 1974;Heie 1980).
3. Reciprocal crosses within and between life cycle variants showed no effect of the type of cross on the number of eggs laid per mating female, their hatching success, or the survival and fecundity of the parthenogenetic females born from eggs (fundatrices). 4. Insect Order ID: Hemiptera (Aphids) Life Cycle –A form of gradual metamorphosis (also called incomplete or simple). Eggs hatch in spring producing parthenogenic females (able to reproduce asexually), which give birth to live young within a few days after birth.
aphids, which can become mature adults within a couple of weeks or so after birth. (Development is always strongly related to temperature.) Adult females may give birth to perhaps 1-5 young per day for their remaining life, which likely will normally be short, perhaps a 3 … The life cycle of many aphids is somewhat unusual and complex. Most species overwinter in the egg stage on the host plant; the eggs hatch into young female nymphs (stem mothers) in the spring, and subsequently reproduce without mating (parthenogenetic reproduction), giving birth to living young.
aphids, which can become mature adults within a couple of weeks or so after birth. (Development is always strongly related to temperature.) Adult females may give birth to perhaps 1-5 young per day for their remaining life, which likely will normally be short, perhaps a 3 … LIFE CYCLE OF THE SUGARBEET ROOT APHID . A relatively new pest entered the sugarbeet production cycle and everyone is interested in the economic impact these insects will have on the crop. Sugarbeet aphids feed primarily on the secondary root systems; although heavy
Although aphids cannot fly for most of their life cycle, they can escape predators and accidental ingestion by herbivores by dropping off the plant onto the ground. Others species use the soil as a permanent protection, feeding on the vascular systems of roots and remaining underground all their lives. Life cycle. Bird cherry (Prunus padus) with its long drooping white flowers (below) is the primary host of Rhopalosiphum padi. The eggs of Rhopalosiphum padi are laid in autumn in the narrow gap between the axillary buds and the stem (see image below).
•The life cycle of honey bees begins when an egg hatches. •During the first stage of its development, the offspring form a digestive system, a nervous system and an outer covering (the exoskeleton). •Each member of a colony develops, after hatching, as an adult over varying durations: –Queens become full-grown adults within 16 days, LIFE CYCLE OF THE SUGARBEET ROOT APHID . A relatively new pest entered the sugarbeet production cycle and everyone is interested in the economic impact these insects will have on the crop. Sugarbeet aphids feed primarily on the secondary root systems; although heavy
A second, abbreviated life cycle consisting of only three generations restricted to witch-hazel was discovered at high elevation (1000 m) in north central and northwestern Virginia. Aphids of both life cycles were sympatric at a middle elevation site. The life cycles and morphology suggest that the two forms are separate species. Life cycle. Bird cherry (Prunus padus) with its long drooping white flowers (below) is the primary host of Rhopalosiphum padi. The eggs of Rhopalosiphum padi are laid in autumn in the narrow gap between the axillary buds and the stem (see image below).
In the process of sucking out plant juices, aphids- like mealybugs and scale - excrete a sweetish, sticky "honeydew" that often turns a moldy black and may lure ants. Aphids also carry viral diseases to plants. Life cycle: Females seem to like enormous families. A single aphid typically gives birth to Pea Aphids Scouting for aphids in pulse crops is conducted using a 15-inch sweep net Western Triangle Ag Research Center 9546 Old Shelby Rd, P.O. Box 656, Conrad, MT 59425; Contact: (406) 278-7707 Threshold Levels Pea Aphid Monitoring Life Cycle Damage Common insect pests in pulse crops Small (about 1/8 inch) Pale to dark green in color with
Aphids suck on sap, causing loss of vigour, and in some cases yellowing, stunting or distortion of plant parts. Honeydew (unused sap) secreted by the insects can cause sooty mould to develop on leaves. In crops such as cotton, the honeydew affects fibre quality. Aphids can also be vectors (carriers) for viruses. ENTFACT-219: Woolly Apple Aphid Download PDF. by Ric Bessin, Extension Entomologist, and John Hartman, Extension Plant Pathologist University of Kentucky College of Agriculture The woolly apple aphid differs from other apple aphids in appearance, life cycle, and the type of damage inflicted.
Tulip bulb aphids (Dysaphis tulipae) can infect many different bulbs in storage. Some aphids may even be found on plant roots (Pemphigus species). Honeysuckle aphid Oleander aphid Life Cycle Most types of aphids do not mate and the females give birth to live nymphs. There is no egg stage. In the process of sucking out plant juices, aphids- like mealybugs and scale - excrete a sweetish, sticky "honeydew" that often turns a moldy black and may lure ants. Aphids also carry viral diseases to plants. Life cycle: Females seem to like enormous families. A single aphid typically gives birth to